Four composite images deliver dazzling views from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory and James Webb Space Telescope of two galaxies, a nebula, and a star cluster. Each image combines Chandra's X-rays — a form of high-energy light — with infrared data from previously released Webb images, both of which are invisible to the unaided eye. Data from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope (optical light) and retired Spitzer Space Telescope (infrared), plus the European Space Agency's XMM-Newton (X-ray) and the European Southern Observatory's New Technology Telescope (optical) is also used. These cosmic wonders and details are made available by mapping the data to colors that humans can perceive.
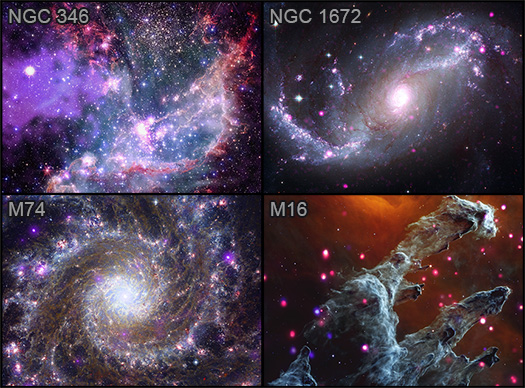
Beginning in the upper left and moving clockwise, the objects are:
NGC 346:
NGC 346 is a star cluster in a nearby galaxy, the Small Magellanic Cloud, about 200,000 light-years from Earth. Webb shows plumes and arcs of gas and dust that stars and planets use as source material during their formation. The purple cloud on the left seen with Chandra is the remains of a supernova explosion from a massive star. The Chandra data also reveals young, hot, and massive stars that send powerful winds outward from their surfaces. Additional data from Hubble and Spitzer is included, along with supporting data from XMM-Newton and ESO’s New Technology Telescope. (X-ray: purple and blue; infrared/optical: red, green, blue)
NGC 1672:
NGC 1672 is a spiral galaxy, but one that astronomers categorize as a “barred” spiral. In regions close to their centers, the arms of barred spiral galaxies are mostly in a straight band of stars across the center that encloses the core, as opposed to other spirals that have arms that twist all the way to their core. The Chandra data reveals compact objects like neutron stars or black holes pulling material from companion stars as well as the remnants of exploded stars. Additional data from Hubble (optical light) helps fill out the spiral arms with dust and gas, while Webb data shows dust and gas in the galaxy’s spiral arms. (X-ray: purple; optical: red, green, blue; infrared: red, green, blue)
M16 (Eagle Nebula):
Messier 16, also known as the Eagle Nebula, is a famous region of the sky often referred to as the “Pillars of Creation.” The Webb image shows the dark columns of gas and dust shrouding the few remaining fledgling stars just being formed. The Chandra sources, which look like dots, are young stars that give off copious amounts of X-rays. (X-ray: red, blue; infrared: red, green, blue)
M74:
Messier 74 is also a spiral galaxy — like our Milky Way — that we see face-on from our vantage point on Earth. It is about 32 million light-years away. Messier 74 is nicknamed the Phantom Galaxy because it is relatively dim, making it harder to spot with small telescopes than other galaxies in Charles Messier’s famous catalog from the 18th century. Webb outlines gas and dust in the infrared while Chandra data spotlights high-energy activity from stars at X-ray wavelengths. Hubble optical data showcases additional stars and dust along the dust lanes. (X-ray: purple; optical: orange, cyan, blue, infrared: green, yellow, red, magenta)
NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center manages the Chandra program. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory's Chandra X-ray Center controls science operations from Cambridge, Massachusetts, and flight operations from Burlington, Massachusetts.
The James Webb Space Telescope is the world’s premier space science observatory. Webb will solve mysteries in our solar system, look beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probe the mysterious structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Webb is an international program led by NASA with its partners, ESA (European Space Agency) and the Canadian Space Agency.
This release features four separate images that combine X-ray data from the Chandra Observatory, and infrared data from the James Webb Space Telescope, and some data from other telescopes like Hubble, Spitzer and XMM-Newton. The dark but colorful, highly detailed, composite images, are presented individually, and in a two-by-two grid.
At our upper left is the NGC 346 star cluster. Here, thousands of specks of light blanket the blackness of space. A ribbon of thick orange cloud runs along the bottom edge of the image, rounds our lower right corner, and streaks up the right side. A similar patch of roiling orange cloud can be found near our upper left. Between these gas plumes, centered near the top of the image, the star cluster is densely packed with specks of white, blue, and purple light. At our left, a large, bright white, gleaming dot is surrounded by purple mist. This is a hot, young, massive star, sending powerful winds outward from its surface. A patch of smaller dots, other young stars, can be found inside a faint purple mist near the center of the image.
Next, in our lower left of the two-by-two grid, is a spiral galaxy like our own Milky Way, known as Messier 74. Shown face-on from our vantage point on Earth, the galaxy's sparkling arms spiral out from a bright white core. The core appears vibrant and alive, and crackles with lightening-like, pale blue light. Glowing, high-energy stars in purple, white, and orange, dot the lengths of the spiraling arms. Webs of murky dust crisscross the space between the curving silver blue arms, also known as dust lanes.
At our upper right of the two-by-two grid is another spiral galaxy called NGC 1672. Also shown face on, this spiral galaxy has two major arms curving away from the bright swirling light at its core. One arm extends to our lower left with a gentle upward curve. The other extends to our upper right with a curve reminiscent of a question mark. Both arms have a cloudy, silver blue quality, and are dotted with bright white and purple stars of varying sizes. In this galaxy, categorized as a "barred" spiral, the arms don’t appear to reach the bright core. The space around the bright pinkish core is a swirl of murky, pale silver cloud.
Finally, at our lower right of the two-by-two grid, is the Eagle Nebula, often referred to as the "Pillars of Creation". Here, tall columns of gray gas and dust emerge from the bottom edge of the image, stretching toward our upper right. Backed by dark orange mist, the cloudy gray columns are surrounded by dozens of soft, glowing, pink and purple dots; massive stars emitting enormous amounts of X-rays. The shapes, hints of movement, and colors in this composite rendering create a dream-like image. The misty orange background suggests a dusky sky, and the glowing pink and purple stars resemble fireflies. Churning with turbulent gas and dust, the columns lean to our right with small offshoots pointing in the same direction. These details evoke an image of yearning cloud creatures at dusk, pointing at something just out of frame.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||

