X-Ray Binaries In Globular Clusters
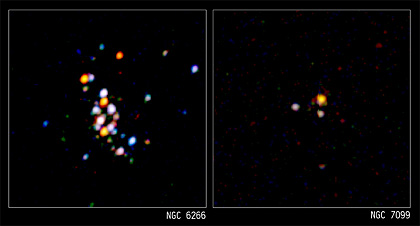
Chandra's unique ability to precisely locate and resolve individual X-ray sources in 12 globular clusters in our Galaxy has given astronomers a crucial clue as to the origin of these sources. Two clusters, known as NGC 6266 (or M62) and NGC 7099 (or M30), are shown here.
A globular cluster is a spherical collection of hundreds of thousands and even millions of stars buzzing around each other in a gravitationally bound stellar beehive that is about a hundred light years in diameter. The stars in a globular cluster are often only about a tenth of a light year apart. For comparison, the nearest star to the Sun, Proxima Centauri, is 4.2 light years away.
Most of the point-like sources in these images are binary star systems containing a collapsed star, such as a neutron star or a white dwarf star, that is pulling matter off a normal companion star. While direct, head-on collisions between stars are rare even in these crowded circumstances, close encounters occur and can lead to the formation of binary star systems containing a collapsed star.
The images illustrate a general trend observed for globular clusters. Clusters such as M62 where the stars are packed very closely together and the rate of close encounters is high have more X-ray binaries than those such as M30 in which close encounters occur less often. This is strong evidence that the X-ray binaries in globular clusters are formed by close encounters.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The two-panel Chandra X-ray Observatory image of the globular star clusters NGC 6266 (left side) and NGC 7099 (right side) displays a dark background with numerous bright dots scattered across the images, resembling multicolored holiday lights. These dots range in size and intensity, with some being brighter and more prominent than others. Some of the bright dots appear to have blurred edges and several concentrated clusters of bright dots are visible. A globular cluster is a spherical collection of hundreds of thousands and even millions of stars buzzing around each other in a gravitationally bound stellar beehive that is about a hundred light years in diameter. Some stars in a globular cluster are only about a tenth of a light year apart. For comparison, the nearest star to the Sun, Proxima Centauri, is 4.2 light years away.
Most of the point-like sources in these images are binary star systems containing a collapsed star, such as a neutron star or a white dwarf star, that is pulling matter off a normal companion star. While direct, head-on collisions between stars are rare even in these crowded circumstances, close encounters occur and can lead to the formation of binary star systems containing a collapsed star.