CXC Home | Search | Help | Image Use Policy | Latest Images | Privacy | Accessibility | Glossary | Q&A
1
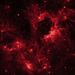
X-ray, Infrared & Optical Images of NGC 1929
These images show a superbubble in the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), a small satellite galaxy of the Milky Way, located about 160,000 light years from Earth. Many new stars, some of them very massive, are forming in the star cluster NGC 1929, which is embedded in the nebula N44. The massive stars produce intense radiation, expel matter at high speeds, and race through their evolution to explode as supernovas. The winds and supernova shock waves carve out huge cavities called superbubbles in the surrounding gas. X-rays from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory show hot regions created by these winds and shocks, while infrared data from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope outline where the dust and cooler gas are found. The optical light from the 2.2m Max-Planck-ESO telescope in Chile shows where ultraviolet radiation from hot, young stars is causing gas in the nebula to glow.
(Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/U.Mich./S.Oey, IR: NASA/JPL, Optical: ESO/WFI/2.2-m)
These images show a superbubble in the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), a small satellite galaxy of the Milky Way, located about 160,000 light years from Earth. Many new stars, some of them very massive, are forming in the star cluster NGC 1929, which is embedded in the nebula N44. The massive stars produce intense radiation, expel matter at high speeds, and race through their evolution to explode as supernovas. The winds and supernova shock waves carve out huge cavities called superbubbles in the surrounding gas. X-rays from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory show hot regions created by these winds and shocks, while infrared data from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope outline where the dust and cooler gas are found. The optical light from the 2.2m Max-Planck-ESO telescope in Chile shows where ultraviolet radiation from hot, young stars is causing gas in the nebula to glow.
(Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/U.Mich./S.Oey, IR: NASA/JPL, Optical: ESO/WFI/2.2-m)
Return to NGC 1929 (August 30, 2012)