Chandra Observes Extraordinary Event
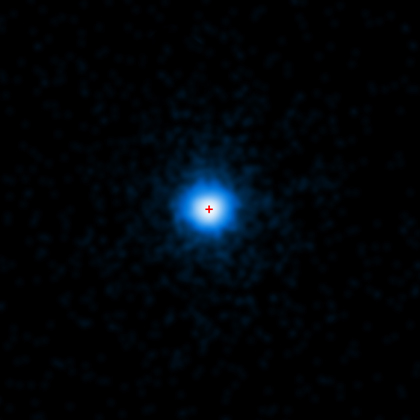
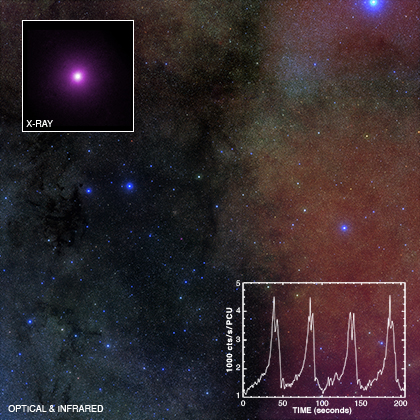
Submitted by chandra on Wed, 2011-04-06 15:31The center of this image contains an extraordinary gamma-ray burst (GRB) called GRB 110328A, observed with NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory. This Chandra observation confirms the association of GRB 110328A with the core of a distant galaxy and shows that it was an exceptionally long lived and luminous event compared to other GRBs.